If you have deployed SCOM Gateway in your environment, or SCOM agent on a workgroup machine, but they can’t communicate with management server, you can refer to the following steps for troubleshooting.
Based on my experience, these troubleshooting steps can help resolve >50% of Gateway/Workgroup communication issues.
Troubleshooting Steps
- Make sure Microsoft Monitoring Agent service is running, and Startup type is set to Automatic on management server and gateway/workgroup.
-
Check the gateway/workgroup status in SCOM console.
-
Check Operations Manager event log
If the certificate is recreated, we should find Event ID 20053 in Operations Manager event log on both the management server and gateway server/workgroup, indicating the certificate was loaded successfully.
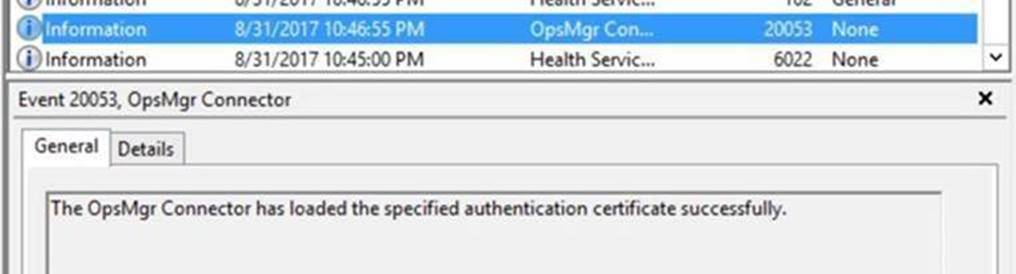
If you find a related warning or error in event log, refer to this blog for explanation: Troubleshoot workgroup/gateway issue with event log
-
Ensure port 5723 is open
On gateway/workgroup:telnet <Management Server FQDN> 5723 - DNS
Make sure that both sides are reachable via hostname (just ping). If it’s not working add the computers in DNS or in the Host file (C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\ETC\Host). -
Check certificate
Computer Certificate:
- Go to both management server and gateway server/workgroup, navigate to HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Microsoft Operations Manager\3.0\Machine Settings and check the value of ChannelCertificateSerialNumber.
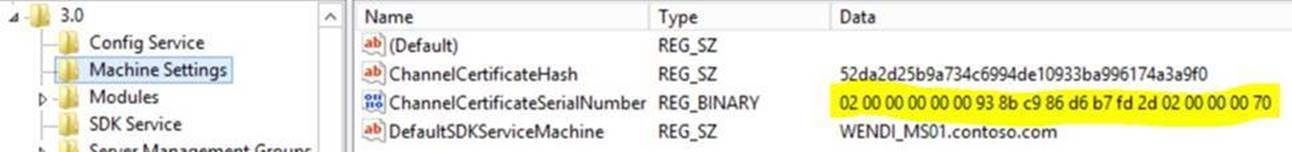
Then, open mmc -> File -> Add or Remove Snap-ins -> Certificates -> Add, select Computer account, then Next and Finish. In Personal -> Certificates, open the certificate that you install on management server/gateway server/workgroup agent, click on Details tab and check the Serial Number. The Serial number and the registry value ChannelCertificateSerialNumber should match each other.
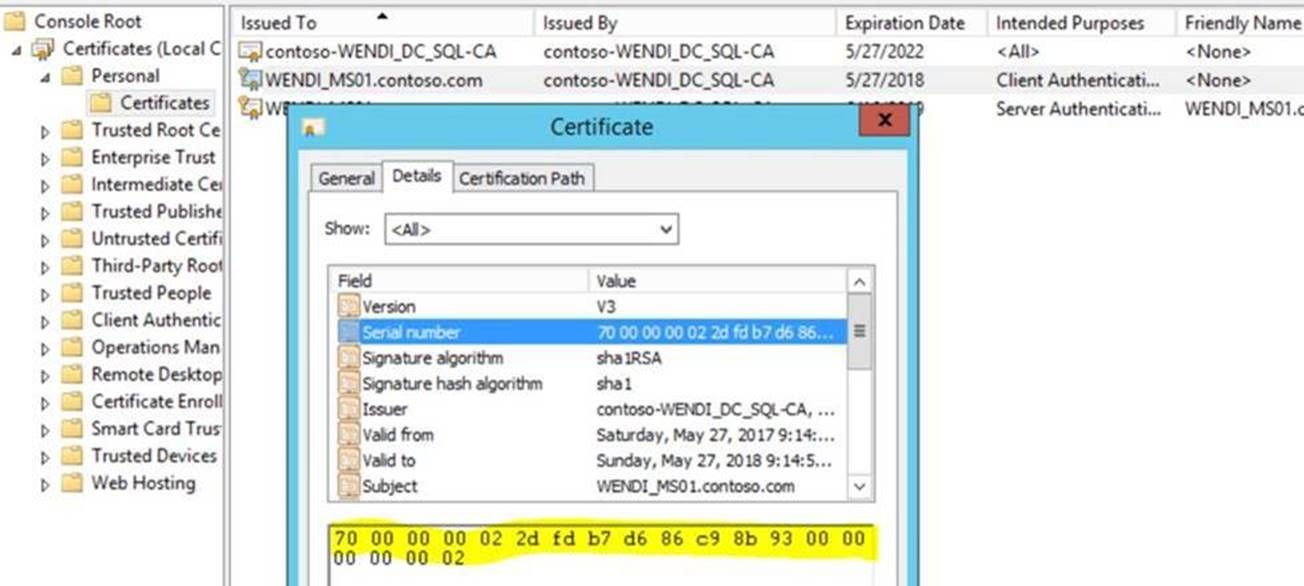
-
Confirm computer certificates on both sides are issued by the same CA.
-
The certificate must includes the private key.
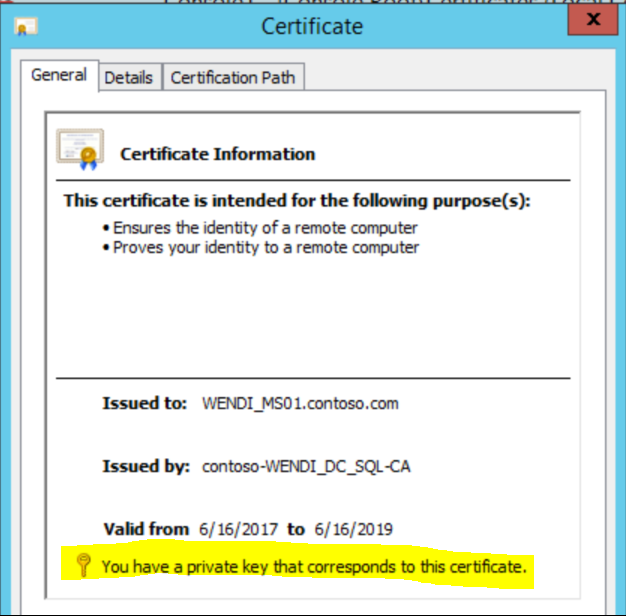
-
The certificate must be trusted all the way to the root (Chain)
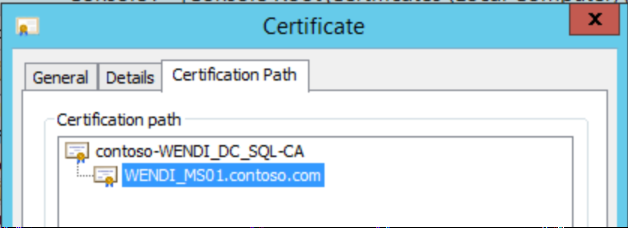
-
The Common Name (CN) value in the certificate’s Subject field must match the FQDN of the computer where you imported the certificate.
-
Ensure the certificate includes both Server Authentication OID and Client Authentication OID in the Enhanced Key Usage property.
-
Check expiration date.
-
Other comments:
Hash Algorithm does not need to be same between source and target. (Ex. SHA1 on MS and SHA256 on GTW works)
Key size can be 2048 and 4096.
Trusted Root Certificate:
Confirm trusted Root Certificate is well imported and can be found under Trusted Root Certification Authorities – Certificates. Check expiration date. - Go to both management server and gateway server/workgroup, navigate to HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Microsoft Operations Manager\3.0\Machine Settings and check the value of ChannelCertificateSerialNumber.
-
On the gateway server, go to HKLM\Software\ Microsoft\Microsoft Operation Manager\3.0\Server Management Group\
\Parent Health Services\0 . Ensure the AuthenticationName and the NetworkName match and is FQDN of management server.In workgroup scenario, the path is HKLM\Software\ Microsoft\Microsoft Operation Manager\3.0\Agent Management Group\
\Parent Health Services\0 -
Ensure the assigned management server in Control Panel is correct.
-
Duplicate SPN
On management server, identify the duplicate SPN. Any duplicate SPN’s will be listed.
setspn -xDelete the duplicate SPN
setspn –d <SPN> <object>Example:
setspn -D http/daserver daserver1 setspn –d host/fscluster member
